End of waste: the cessation of the qualification of waste, what it is and how it can be obtained by following the current legislation.The recycling system in Italy is regulated by a series of rules that allow material recovery as required by European standards and in full compliance with the principles of the Circular economy, seeing in renewal of matter with waste recycling one of its founding pillars. Legislative Decree 152/2006 – Consolidated environmental text – is the regulatory scheme that dictates the definitions, conditions and necessary authorizations to be able to treat a waste and transform it into a new material that can be used in new production cycles. It is therefore necessary that waste, in order to cease to be such, follows a precise scheme of treatment and control regulation called End of Waste.
The End of Waste in Italian legislation
“End of waste“, or better still – since substances and objects cannot disappear – “cessation of waste status“. This is because the legislation provides that a substance that has become “waste” and therefore must be managed in compliance with the onerous sector regulations, can, after having been successfully subjected to a “recovery” process, return to being managed as a “non-waste”. Directive 2008/98 / EC on waste (implemented in Italy with Legislative Decree 152/2006 in article 184-ter) establishes for this purpose the four general conditions to be respected so that the cessation of the qualification of waste occurs, postponing the precise definition of the “detailed” conditions for the individual types of waste to subsequent detailed measures. Directive 2018/851 / EU has recently been included in this framework, which, in revising the waste directive as a whole, also modified the rules for the End of waste.
The changes must be implemented by 5 July 2020. Article 6 of Directive 2008/98 / EC in the version in force before the entry into force of Directive 2018/851 / EU, entrusted primarily to the European institutions the task of dictating specific criteria for individual types of waste in particular: “ at least for aggregates, paper and glass waste, metals, tires and textile waste “. However, the European Union published only three Community regulations between 2011 and 2013 concerning only two of the six types envisaged (metals and glass).
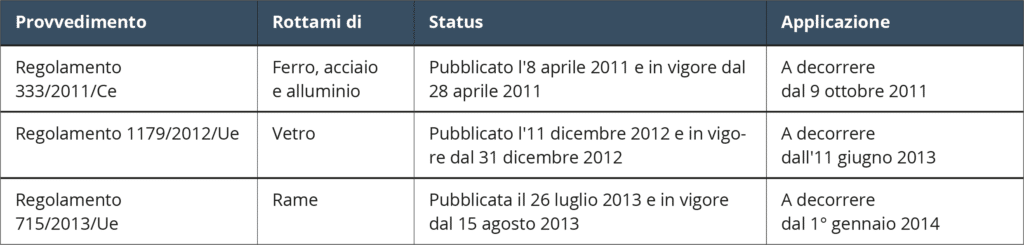
Since the European Union has not published Community End of Waste, the rule gives each member state the right to build End of Waste “ case by case for specific types of waste through one or more decrees” .
Today, however, only three End of Waste have been issued:

Discussions are currently underway between Trade Associations and the Ministry of the Environment for the construction of other End of Waste that will help unblock the recycling chain.
The construction of an Authorization scheme for EoWs
A waste treatment plant with current legislation, may have “the End of Waste authorization” to be able to treat a waste and transform it into new usable recycled material . This authorization can follow a national scheme (such as the 3 currently published by the Ministry of the Environment), or request authorization on a case-by-case basis from the competent management Body. In order to obtain it, however, the authorization request must follow a precise regulation scheme that follows the updated article 184-ter of Legislative Decree 152/2006.
For the construction of an End of Waste authorization it is therefore essential to always take into consideration the general conditions (paragraph 1 of the article) and the detailed criteria (paragraph 3 of the article), essential elements to define, collect and catalog to be able to have a clear waste treatment procedure in order to cease such qualification. During the discussion with the authorization body, it is important to have a standardization of the procedure to ensure homogeneity throughout the territory and improve the effectiveness of the subsequent compliance control of the management and production of EoW. The table below summarizes the necessary conditions to be defined for the construction of the End of Waste authorization:

Another element to analyze and catalog are the detailed criteria for the treatment, summarized in table 2:

These two tables collect the contents necessary for a good construction of an End of Waste authorization that can be presented to the authorization body.
Download Unit 3.5 (to download the pdf you must subscribe to the website/newsletter by releasing your email)
Learn more about the other Didactic Units
INTELLECTUAL AND INDUSTRIAL PROPERTY RIGHTS – LIMITATION OF USE
© Copyright Reserved – This Educational Unit and the related editorial content conveyed are the subject of intellectual and industrial property of Circularity Srl – Benefit Society and as such protected.